Search Results for: up-regulation physiology
Physiology
Definition noun (1) A branch of biology that deals with the functions, mechanisms, and activities of organisms at the... Read More
Up-regulation physiology
up-regulation (physiology) process that increases ligand/receptor interactions due to an increase in the number of available... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
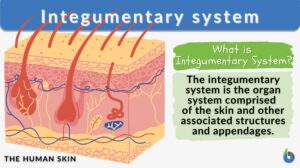
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
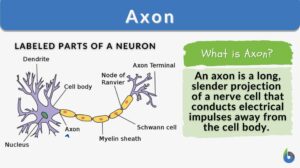
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
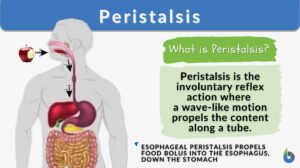
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
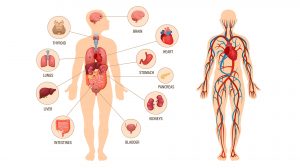
The Human Physiology
Physiology is the study of how living organisms function. Thus, human physiology deals specifically with the physiological... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
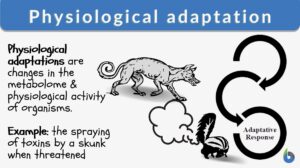
Physiological adaptation
If we look over evolutionary history, we find that it’s neither the most genius and intelligent nor the strongest and the... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
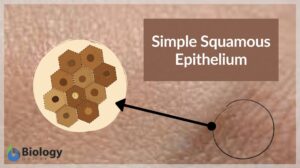
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Sugar Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Regulation As described in Cell Biology tutorials, the body requires volumes of glucose in order to create ATP.... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo MinnsSubmitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009.Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Down-regulation
Down-regulation (Science: physiology) development of a refractory or tolerant state consequent upon repeated administration... Read More
Feedback regulation
Feedback regulation (Science: physiology) control mechanism that uses the consequences of a process to regulate the rate at... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Deglutology
Definition noun The scientific or medical study of the processes and pathophysiology of deglutition Supplement Deglutology... Read More
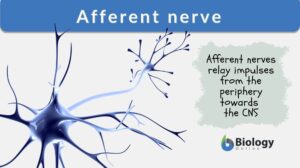
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
Antagonistic Muscle
Definition of Antagonistic Muscle What does the term “antagonistic” mean? As the name suggests, the word antagonistic... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More